
Is any amount of alcohol consumption advisable? How much to drink according to age? Lancet study answers | The Financial Express

Risk thresholds for alcohol consumption: combined analysis of individual-participant data for 599 912 current drinkers in 83 prospective studies - The Lancet

The Lancet on X: "Minimum unit pricing for alcohol was associated with a 13% decrease in deaths from alcohol consumption in Scotland, according to a new study. Read this and more in

Alcohol consumption and cardiovascular disease, cancer, injury, admission to hospital, and mortality: a prospective cohort study - The Lancet

The Lancet: Alcohol consumption carries significant health risks and no benefits for young people; some older adults may benefit from drinking a small amount of alcohol : r/india

National, regional, and global burdens of disease from 2000 to 2016 attributable to alcohol use: a comparative risk assessment study - The Lancet Public Health

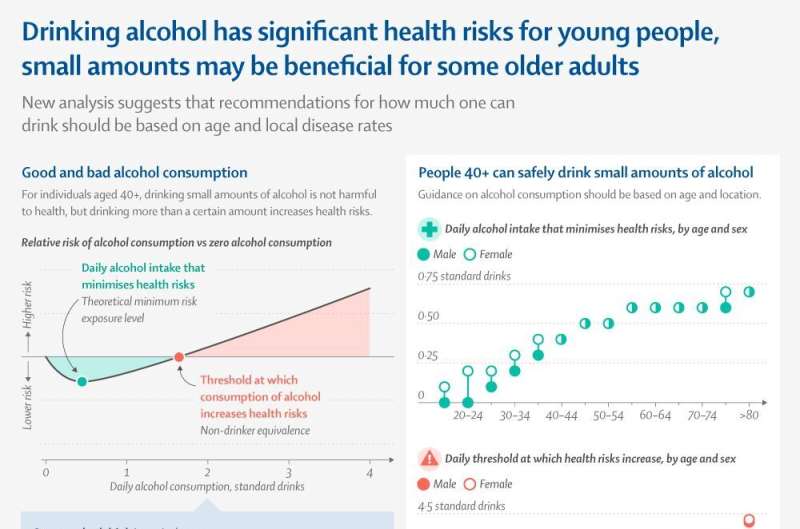
Young people face higher health risks from alcohol consumption than older adults, according to a new analysis published in The Lancet. The analysis from the Global Burden of Disease is the first

Population-level risks of alcohol consumption by amount, geography, age, sex, and year: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2020 - The Lancet

Risk thresholds for alcohol consumption: combined analysis of individual-participant data for 599 912 current drinkers in 83 prospective studies - The Lancet

The Lancet - Alcohol-related liver disease | NEW The Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology Series Excessive alcohol consumption is one of the leading causes of liver disease and the seventh leading cause of

The Lancet on X: "In 2020, an estimated 1.34 billion people consumed harmful amounts of alcohol. On the cover, authors of a new #GBDStudy issue a call for targeted action: https://t.co/W5Vm8Y9nEr https://t.co/xUMXnMyK9U" /








)

